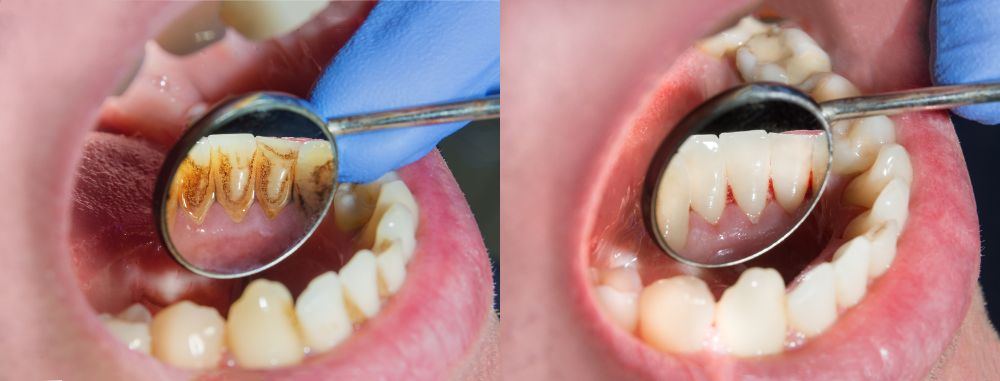
Periodontal disease also known as gum disease, is a serious infection of the gums and its surrounding tissue. It is usually caused by bad dental hygiene such as poor brushing and flossing habits, causing plaque to build up on the teeth and harden.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
- Bad breath
- Swollen or sore gums
- Tender or bleeding gums
- Painful chewing
- Receding gums
- Sensitive teeth
- Loose teeth
Types of Periodontal Diseases
- Chronic periodontal disease
Caused by a plaque build-up, leading to gum and bone deterioration. Diagnosing chronic periodontal disease is important in its early stages to prevent severe and irreversible damage to the protective and supportive structures of the tooth. If left untreated, it may eventually lead to tooth loss.
- Aggressive periodontal disease
It usually affects young people and can run in the family. Once diagnosed, aggressive periodontal disease can progress rapidly and eventually leads to tooth loss.
- Necrotizing periodontal disease
A rare form of infection affecting the mouth, causing the necrosis or death of gum tissue and bone. It is more commonly found in individuals with weakened immune systems, and can also lead to tooth loss, if left untreated.
Long-Term Risks of Periodontal Disease
If left untreated, periodontal disease will affect your health as well. Periodontal disease has also been found to increase one’s blood sugar, posing a problem especially for people with diabetes. In fact, diabetic patients are more likely to develop periodontal disease. Even if you do not have diabetes now, the mere presence of periodontal disease can signal the development of diabetes later in life.
Moreover, research has shown that the same oral bacteria that cause tooth decay was found in the plaques that lines your arteries, which is a major contributing factor to many heart diseases. This is because as bacteria continues to grow, it can leach into your bloodstream, travel throughout your body, leading to health problems.
In response to these bacteria, your body reacts by sparking an inflammatory response. This causes an aggravation of other inflammation-causing illnesses, such as rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory disease, kidney cancer, and even blood cancers like leukemia.
Since periodontal disease can cause so many health problems, it decreases your overall immune response, putting you at a higher risk for other infections.
Treatments for Periodontal Disease
The main goal of treating periodontal disease is to control the infection. The treatments will vary, depending on the severity of the gum disease. In addition, do practice good oral hygiene, which includes brushing and flossing at least twice per day and visiting your dentist regularly.
If you still experience any of the mentioned symptoms, don’t wait to make an appointment with your dentist. Having an experienced dentist perform the procedure will help to ensure that you get the results you want. Call Dr. Alex Rubinov at (718) 253-0800 today to make an appointment.