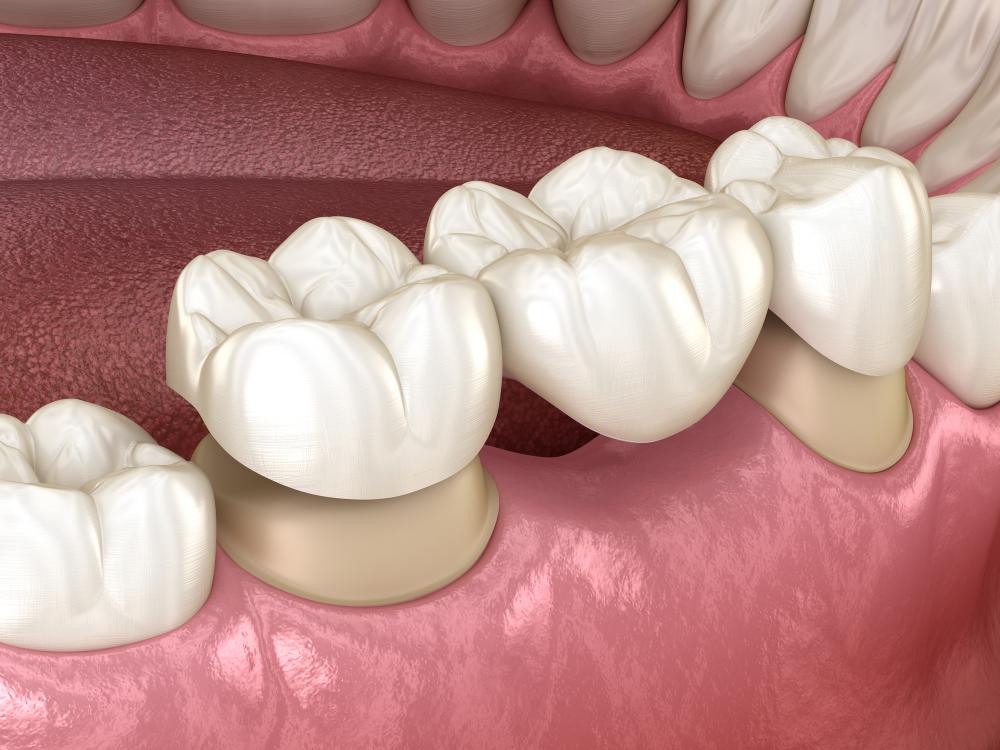
A dental bridge is a standard solution for replacing missing teeth. Dr. Alex Rubinov, a renowned cosmetic dentist in New York City, explains that a dental bridge ‘bridges’ the gap where one or more teeth may have been. The goal of a bridge is to restore both the function and appearance of teeth. In its basic form, a dental bridge consists of one or more false teeth, known as pontics, which are held in place by dental crowns. This arrangement creates a seamless look, blending the artificial teeth with the natural ones. Dr. Rubinov stresses the importance of replacing missing teeth to avoid long-term problems and maintain oral health. While the concept of a dental bridge is simple, various factors can influence the overall dental bridge cost, which Dr. Rubinov will explore further.
Key Factors Affecting the Cost of Dental Bridges
When considering a dental bridge, it’s essential to understand the key factors that influence the dental bridge cost. Dr. Alex Rubinov points out several variables that play a role.
The number of missing teeth the bridge will replace directly impacts the cost. More missing teeth require a bigger bridge, which involves more material and labor.
The materials used for the bridge also affect the price. Porcelain and ceramic bridges offer a more natural appearance and are more expensive than metal or acrylic bridges.
Another factor is the complexity of the dental work required. The overall cost will increase if additional procedures like tooth extraction or oral surgery are needed before placing the bridge.
Labor and geographic location are also critical factors. Specialized work from highly skilled dentists like Dr. Rubinov, especially in cities like New York, can be more costly than in other regions.
Types of Dental Bridges and Their Costs
There are several types of dental bridges, and each comes with a different cost structure. Dr. Alex Rubinov explains these types, helping patients understand their options.
Traditional bridges, the most common type, involve creating a crown for the tooth with a pontic in between. These are usually made of porcelain fused with metal or ceramics and are used when natural teeth are present on both sides of the gap.
Maryland bonded bridges, also referred to as resin-bonded bridges or porcelain-fused-to-metal bridges, are dental prostheses made up of porcelain or plastic teeth and gums. These are affixed to a framework made of either metal or porcelain, with wings made of either porcelain or metal on each side of the bridge that are bonded to your natural teeth for support.
The cost of each type of bridge varies. Traditional bridges are typically more expensive than Maryland bridges due to the complexity and materials used. Cantilever bridges may also vary in cost, depending on the specific situation and materials.
Dr. Rubinov emphasizes the importance of consulting with a dental professional to determine the best type of bridge for your specific needs and get an accurate cost estimate. Each patient’s situation is unique, and a personalized consultation is critical to making the right decision for your oral health and budget.
Price Variations by Geographic Location
The dental bridge cost can also vary significantly based on geographic location. Dr. Alex Rubinov points out that the cost of living and the average market rates for dental services in a particular area play a big role in determining the price of dental bridges.
In larger metropolitan areas, like New York City, where Dr. Rubinov practices, prices for dental procedures are generally higher. This increase is due to the higher costs of running a dental practice in these areas, such as rent, utilities, staff salaries, and equipment. Additionally, dentists in urban areas might have more specialized training and use more advanced technology, which can also contribute to higher costs. Conversely, the cost of dental procedures, including dental bridges, may be lower in smaller towns or rural areas. This often reflects these regions’ lower operational costs and different economic dynamics.